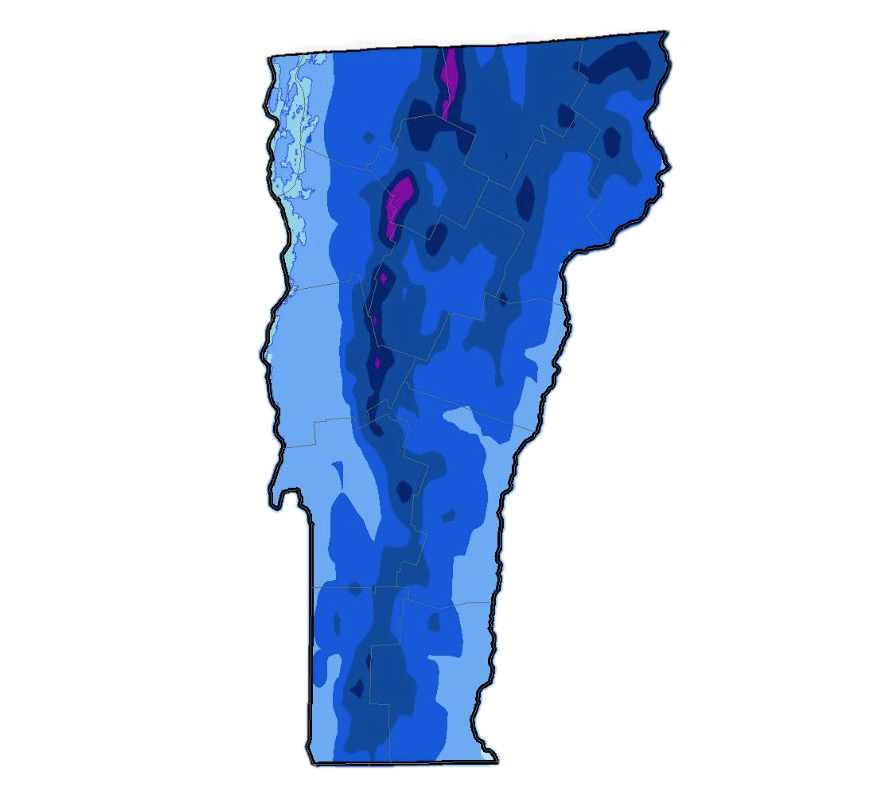
How much snow does Vermont get?
Vermont receives more snow than any other state, averaging 54 days of snowfall and 89 inches of snow per year. When you look at the US average snowfall by state you can see the combination of factors that push Vermont to the top of the list.
First, Vermont lacks low-lying and warmer coastal areas to bring the state-wide snowfall average down. While the eastern shore of Lake Champlain has the lowest annual snowfall average of any part of the state, it’s much colder compared to areas of Long Island which lowr the statewide average for neighboring New York.
Second is Vermont’s nearly ideal location for capturing snow from coastal nor’easters, that can bring large amounts of snowfall in a single storm. While the state is relatively near the coast, it’s not on the coast, and often when storms travel up the eastern seaboard in winter, most or all of the precipitation in Vermont falls as snow.
Finally is the impact of Vermonts unique topography. Orientation of Vermont’s mountains are nearly perfect for capturing snow from synoptic, orographic and even lake effect events.
The Green Mountain Spine
The Green Mountains have a dramatic impact on Vermont snowfall. The effect can be explained by the relationship between the generally north-south orientation of the range and the direction of the prevailing winds. You can clearly see the impact of the spine in the snowfall map above.
In each case, the topography of the Green Mountains — and the effects of orographic lift — work to wring out the most snow from each of these three storm tracks.
One significant difference is that in a coastal nor’easter, during the peak of the storm, the windward and leeward sides are reversed with the eastern slope receiving the bulk of the precipitation. However after the storm passes the western slopes can be favored again, with what is known as “wrap around” snowfall.
Orographic Lift and Snowfall
Orographic precipitation can fall as rain or snow depending on the season and temperature profiles. Orographic snowfall is produced when moist air is lifted as it moves over a mountain range. In winter, as mountains force the air to rise, it cools and orographic clouds form producing snow.
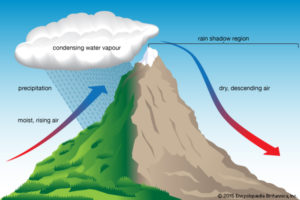
Most of the snow falls on the windward side of the mountain. On the other side of the mountain, snowfall is usually much less as the much of the moisture has already been deposited, and the air is now moving downslope, which reduces snowfall further.
The heaviest orographic effects occur when slopes are perpendicular to prevailing winds and weather patterns. While single mountains and individual slopes can produce orographic snow, when mountains are organized in a range the effect is much stronger. In this case there is no way for moisture-laden air masses to skirt the slopes.
This is why the Green Mountains are so efficient at producing snow, and why Vermont ski area snowfall is generally 100 inches more each season than that of ski areas in New York or New Hampshire.
While the Green Mountain spine generally runs north-south it actually bends subtly to the east at the northern end of the range. This orientation is actually just a bit more productive than the orientation of the southern end of the spine. This, combined with colder temperatures to the north, and the impact of some additional moisture that comes off Lake Champlain, explains why the ski areas of northern Vermont record even higher snow totals than those in southern and central Vermont.
Vermont Snowfall by Location
| Days Snow/Yr | Town/Place | Avg Snow/Yr” |
| 85 | Mount Mansfield | 244″ |
| 66 | Smugglers Notch | 139″ |
| 58 | South Lincoln | 124″ |
| 55 | Newport | 96″ |
| 56 | St Johnsbury | 87″ |
| 47 | Essex Junction | 85″ |
| 54 | Burlington | 81″ |
| 44 | St Albans | 81″ |
| 31 | South Hero | 48″ |
| 50 | Montpelier | 94″ |
| 27 | Rochester | 78″ |
| 39 | Cavendish | 85″ |
| 28 | Woodstock | 81″ |
| 34 | Rutland | 73″ |
Vermont Snowfall by Month
When does it snow in Vermont?
| Month | Mean Snowfall” |
| January | 17.3″ |
| February | 16.1″ |
| March | 13.4″ |
| April | 04.0″ |
| May | 00.1″ |
| June | 00.0″ |
| July | 00.0″ |
| August | 00.0″ |
| September | 00.0″ |
| October | 00.3″ |
| November | 06.2″ |
| December | 15.6″ |
Sources:
• worldpopulationreview.com
• ncdc.noaa.gov
• Orographic snowfall image courtesy britannica.com
• Snowfall per month for BTV 1892-2022 weather.gov/btv/
• Scott Braaten